What Is the Purpose of Each Stage of Steam Turbine Warm-up?
Low Speed Warm-up
The primary goal of low-speed warm-up is to gradually heat the steam turbine's components. This process increases the temperature of the metal cylinder and reduces thermal stress caused by temperature variations within the steam turbine's metal parts.
Medium Speed Warm-up
The aim of medium-speed warm-up is to heat the rotor to reach the low-temperature brittleness transition temperature (where the rotor's center achieves or exceeds 150 degrees Celsius). This prevents low-temperature brittleness in the rotor, ensuring safe power generation post grid connection.
Low Load Warm-up
The main objective of low-load warm-up is to control the expansion differences within the steam turbine. This ensures even heating of the steam turbine, preventing dynamic and static friction due to uneven temperature distribution.
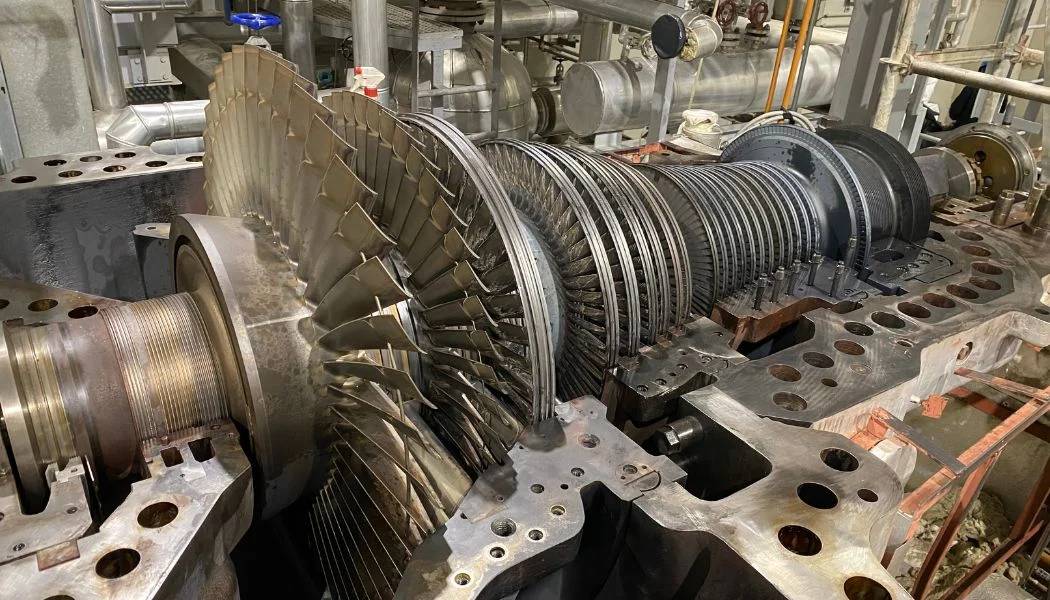
Extended warm-up times during cold starts serve several key purposes:
Increase Lubricating Oil Temperature
The lubrication system circulates to raise the lubricating oil temperature, ensuring the establishment of the bearing oil film.
Additional reading:4 Tips for Choosing a High-Quality Odm Round Steel Flat Iron
Even Temperature Distribution
Gradual temperature increase in the turbine flow parts ensures even expansion, minimizing temperature differences. This prevents dynamic and static friction, extends metal lifespan, avoids thrust tile burning, and reduces shaft system vibration.
Moisture Removal and Insulation Improvement
The generator assists with ventilation, removing moisture and improving insulation. This ensures uniform expansion of wire rods and prevents local stress damage, prepping the unit for grid connection during the warm-up phase.
In contrast, hot start warm-up times are shorter. The speed should be increased to connect to the grid quickly to prevent the cylinder from cooling excessively. If steam pressure is high and the temperature is normal, monitor cylinder temperature changes during acceleration. Should the cylinder temperature drop and the high adjustment valve be minimally opened, the steam intake may be insufficient for cylinder heating.
In such instances, increasing the speed promptly boosts steam intake, ensuring better cylinder heating.



